Transformimet gjeometrike mund ti zbatojme ne nje cikel heresh mbi objekte te ndryshem dhe kjo lehteson mjaftueshem vizatimin e disa objekteve identik ne pozicione , kende apo madhesi te ndryshme.
Ushtrim: Ndertoni nje program qe vizaton nje rreth dhe e zhvendos ate 15 here me 20 njesi ne boshtin x
#include<gl/glut.h>
#include<math.h>
#define
PI 3.14
GLint n=100;
void rrethi(GLfloat x, GLfloat y, GLfloat rreze){
GLint i;
GLdouble theta;
glBegin(GL_POLYGON);
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
theta=2*PI*i/n; //kendi ne
radian
glVertex2f(x+rreze*cos(theta),
y+rreze*sin(theta));
}
glEnd();
}
void
Display()
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
for(int i=0;i<15;i++)
{
glTranslatef(20,0,0);
rrethi(20.,20.,10.);
}
glFlush();
}
void
init()
{
glClearColor(1.0,0.0,0.0,1.0);
glViewport(0,0,500,500);
gluOrtho2D(0.0,500.0,0.0,500.0);
}
int main(int argc, char*
argv[])
{
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE|GLUT_RGB);
glutInitWindowSize(400,400);
glutCreateWindow("Test");
init();
glutDisplayFunc(Display);
glutMainLoop();
}
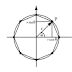
Ushtrim: Ndertoni nje program qe vizaton nje elips dhe e rrotullon ate 12 here me kend 30 grad
rreth qendres
#include<gl/glut.h>
#include<math.h>
#define
PI 3.14
GLint n=100;
void elipsi(GLfloat x, GLfloat y, GLfloat rx, GLfloat ry){
GLint i;
GLdouble theta;
glBegin(GL_POLYGON);
for(i=0;i<n;i++){
theta=2*PI*i/n; //kendi ne
radian
glVertex2f(x+rx*cos(theta),
y+ry*sin(theta));
}
glEnd();
}
void
Display()
{
glClear(GL_COLOR_BUFFER_BIT);
for(int i=0;i<12;i++)
{
glRotatef(30.,0,0,1);
elipsi(200.,100.,50.,30.);
}
glFlush();
}
void
init()
{
glClearColor(0.6,0.4,0.3,1.0);
glViewport(-400,-300,500,500);
gluOrtho2D(-400.0,500.0,-400.0,500.0);
}
int main(int argc, char*
argv[])
{
glutInitDisplayMode(GLUT_SINGLE|GLUT_RGB);
glutInitWindowSize(500,500);
glutCreateWindow("Test");
init();
glutDisplayFunc(Display);
glutMainLoop();
}








0 comments:
Post a Comment